Summer camps have long been described as places where children can benefit from eschewing certain aspects of modern life, where children, for example, can “return to nature,” practice “physical fitness,” or discover “spiritual truths.” Through the generations, as our society has evolved away from some social or cultural norm, parents have sought a way to provide their children access to what they feel is being lost. In this way, camps have happily served as repositories of tradition, havens from the inadequacies and perils of unchecked “progress” accepted by society.
In recent years, a new threat of modernity has risen to the top of the list. It’s not simply “technology,” computers, television or the Internet, in the broadest sense, but it’s related these. It’s the smartphone, in particular the smartphone when in the hands of a child or adolescent.
Professor Jean M. Twenge (Dept. of Psychology at San Diego State University), who researches generational differences, has published a new book that explores how the introduction of the smartphone, its now near ubiquity among teenagers and other young people, correlates with a number of serious public health concerns. The book is: iGen: Why Today’s Super-Connected Kids Are Growing Up Less Rebellious, More Tolerant, Less Happy— and Completely Unprepared for Adulthood —and What That Means for the Rest of Us. She also just published an article in The Atlantic adapted from the book: “Have Smartphones Destroyed a Generation?“
I want to encourage you to read the article, in fact STRONGLY encourage you, because I think you will find it informative, and perhaps troubling if not horrifying. Working at the level of demographics, Professor Twenge began to notice “abrupt shifts in teen behaviors and emotional states” beginning five years ago in 2012, the year when “the proportion of Americans who owned a smartphone surpassed 50 percent.” Today in 2017, almost 75% of American teens own smartphones and have begun to use these devices as a major means through which they interact with the world. What it means to “socialize” for today’s teens is mostly mediated, technologically filtered, by their smartphones. Increasingly these days, adolescents are doing less, meeting and hanging out less, and instead spending free time in virtual spaces texting and sharing Snapchats and other social media messages. Sadly, this often means our kids typically spend hours each day “on their phone, in their room, alone and often distressed.”
Research results pointing to troubling psychological and social trends affecting teens are stacking up. Teens getting together with friends has dropped, as has their interest in driving a car, alcohol consumption, dating, and even sex. While these trends are helping keep kids more physically safe— less drinking and driving, and teen pregnancies, for example — they also show adolescents spending more time alone, indoors and on their phone. Research data is showing teenagers who spend hours using social media are more likely to report being unhappy, lonely, and tired (sleep-deprived). More troubling still is the correlation between smartphone use and depression and suicide. As smartphone use has increased since 2012 among teenagers, so has the suicide rate, now reaching a 40-year high. It’s clear that with the rise of adolescents’ smartphone use, particularly with respect to social media, their behavior and attitudes, their approach to the complexities of life, their expectations and desires, their talents and ambitions, are all changing.
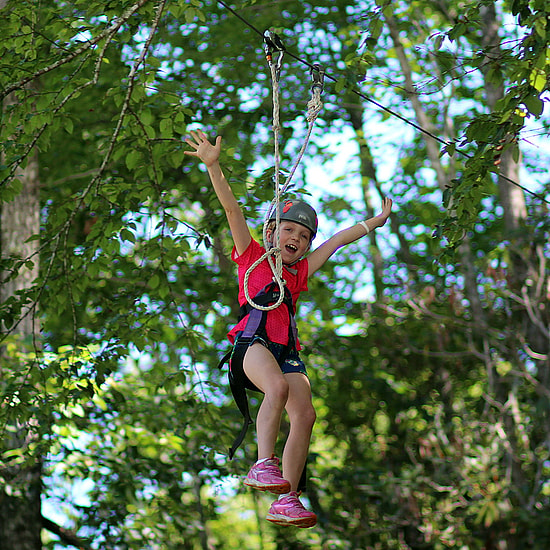
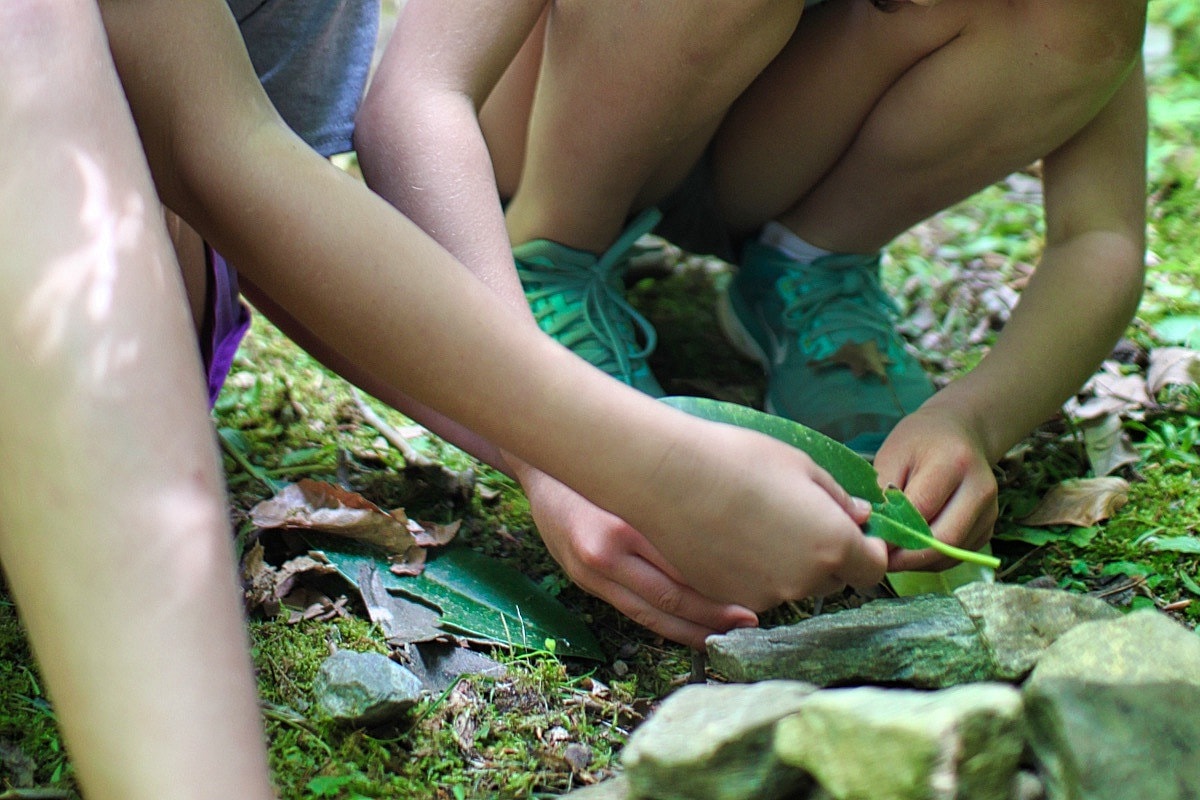
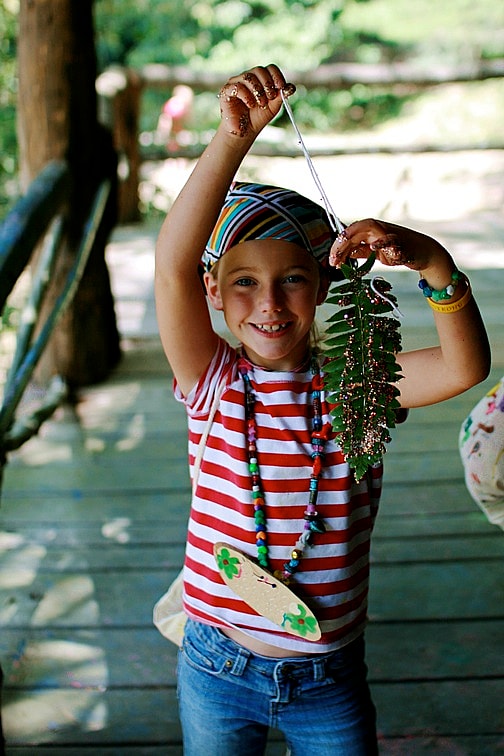
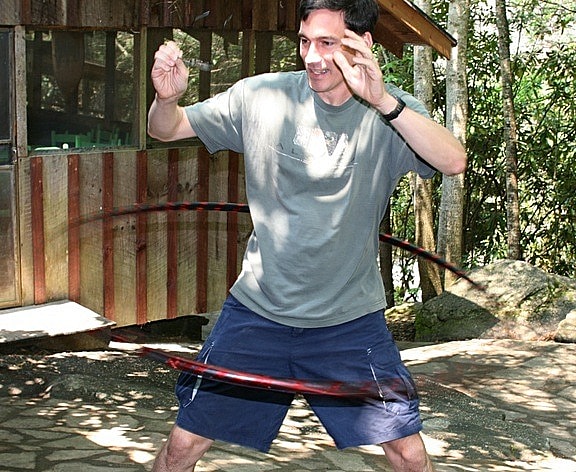
Bringing this back to camp, it should be obvious what Rockbrook provides: a life unfiltered by smartphone technology, one filled with the experience of real friendships, bodily inter-action, discovery and exploration of the natural world. Being at camp means actually doing things. It means children using and stimulating all their senses, not just the narrow idealized encounters available via a screen, no matter how “smart” it is. Camp provides daily opportunities to practice being real, taking managed risks, and creating enthusiastically. Life within a caring community like Rockbrook needs no technology to enliven deeper layers of our humanity, our sense of humor, our awareness of others’ needs, and our innate ability to see beauty in the tiniest detail. For all these reasons and more, camp is a “happy place” for children.
Professor Twenge’s research and writings suggest we should limit our kid’s access to smartphones during their formative years. Kids need rich experiences, face-to-face friendships, the challenges and rewards provided by real life. Handing them a smartphone or tablet robs them of that. Ironically, this communication device isolates teenagers, significantly narrowing who they are and most likely who they will become.
Again, thank goodness for camp, a (smartphone-free) place where kids get what they need, truly enjoy themselves, and grow beautifully.